45 dosage calculations from medication labels
Pharmacology - Drug Dosage Calculation Unit Test # 2 - ProProfs 1. The physician ordered 120 mcg of medication. Onquid suspension of 0.06 mg/ml. How many ml will the nurse administer? A. 1 ml B. 0.5 ml C. 2 ml D. 1.5 ml 2. The patient was ordered to take azithromycin 2 g PO as a single dose. The available stock is 250 mg tablets. The nurse will give: A. 6 B. 2 C. 4 D. 8 3. Pharmacy Calculations - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf 1 solid ounce = 30 g 1 tablespoon = 15 mL 1 teaspoon = 5 mL 1 liquid oz = 30 mL BSA (m^2) = [Height (inches) x Weight (lbs)/3131]^1/2. [11] Male: IBW = 51.65 kg + 1.85 kg/inch of height greater than 5 feet Female IBW = 48.67 kg + 1.65 kg/inch of height greater than 5 feet Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Comment on this article.
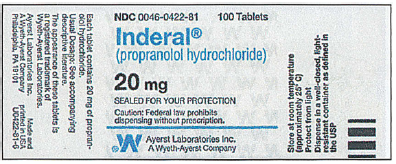
› math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Reading Medication Labels and Calculating Dosages Reading Medication Labels . Before we can even begin to calculate how much medicine to give a patient, we must be able... Sample Medication Labels. Concentration: Each capsule is 120 mg. Notice that the label just says 120 mg, but does not... ...
Dosage calculations from medication labels
Medications | Health Literacy | CDC Medication Labels. A study published in 2013 external icon finds a patient-centered label was better at preventing participants from exceeding the maximum dose in 24 hours, compared to a standard label. The patient-centered label did not significantly reduce other dosing errors such as taking more than two pills at a time and waiting fewer than four hours between doses. Clinical Calculations: Module 5: Parenteral Medications You will calculate the correct amount of injectable medications to give a client. Assume all questions ask for the amount per dose unless instructed otherwise. Equivalents to know You should now know all your commonly used equivalents. Rounding rules to know You will continue to use the rounding rules for numbers >1 and <1. Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method Article A basic formula, solving for x, guides us in the setting up of an equation: D/H x Q = x, or Desired dose (amount) = ordered Dose amount/amount on Hand x Quantity. For example, a provider requests lorazepam 4 Mg IV Push for a patient in severe alcohol withdrawal. The clinician has 2 mg/mL vials on hand.
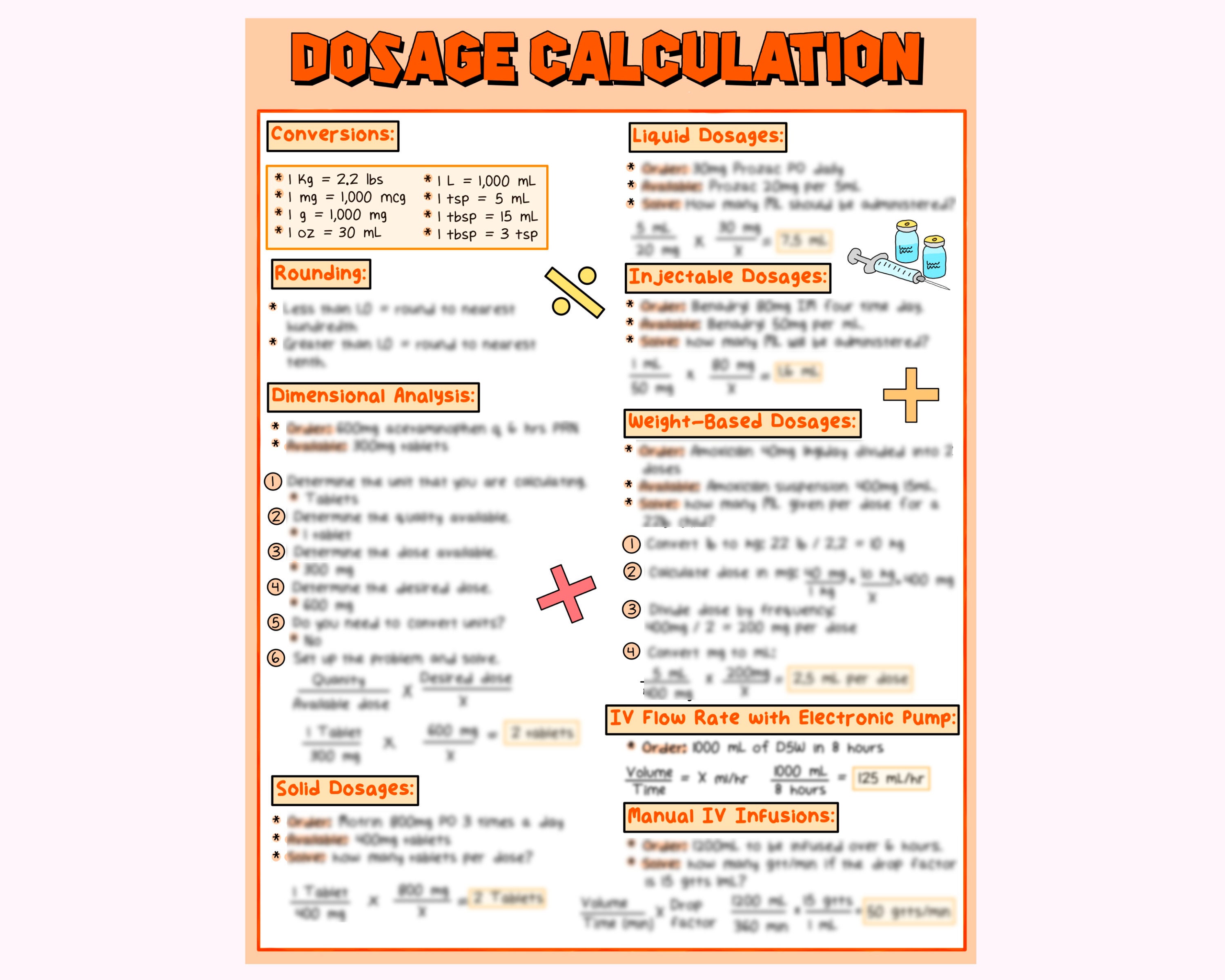
Dosage calculations from medication labels. VASG Drug Dose Charts Drug Dose Charts. Drug dose charts are meant to be a convenience and safety enhancement measure. Staff members can use the chart to find the correct drug volume for a patient of a given size. These charts should be printed in color then placed in plastic sheet protectors and organized alphabetically in a binder. DailyMed The National Library of Medicine (NLM)'s DailyMed searchable database provides the most recent labeling submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) by companies and currently in use (i.e., "in use" labeling). DailyMed contains labeling for prescription and nonprescription drugs for human and animal use, and for additional products such as medical gases, devices, cosmetics, dietary ... Common Medical Conversions: List & Calculator - Drugs.com To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, take the Celsius temperature and multiply it by 1.8, then add 32 to obtain the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales meet at -40°. Above -40°, Fahrenheit temperatures are always higher than corresponding Celsius temperatures, and below -40°, Fahrenheit temperatures are lower ... Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Drug Calculations Quiz Questions With Answers - ProProfs 1. The doctor ordered Magnesium Sulfate 2gm/ hour IV. Magnesium Sulfate come in 40gm/1000mL IV bottle. You would set your pump at _____mL/hour. A. 50 mL/hr B. 60 mL/hr C. 55 mL/hr D. 53 mL/hr 2. The physician ordered Ritodrine IV 70mcg/min. The pharmacy sent up Ritodrine 150mg premixed in 500mL D5W. You would set your IV pump at ________mL/hour. A. Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into the equation in the numerator to cancel out the unwanted labels. Repeat this step sequentially until all unwanted labels are canceled out. Step 4. Multiply numbers across the numerator, then multiply all the numbers across the denominator. Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and Reconstituted ... Your charge nurse recommends that you use 1.8 ml of sterile water to reconstitute the medication to reduce the volume to be injected. How many ml will you give per dose? SF = 2 g AU = ml per dose Equivalents: 1 g = 1000 mg 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label) A Simple Guide to Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians A simple formula to calculate dose dispersed is as follows: dose on hand multiplied by dose dispersed equals dose ordered. In this case, 250 mg x D equals 500 mg, where D represents the dose to...
Xeloda and dosage: Strengths, form, when to take, and more The recommended Xeloda dose for metastatic breast cancer in certain situations is 1,250 mg/m 2. The dosing schedule for Xeloda is two times per day for 2 weeks, followed by 1 week of no treatment ... › drug-dosage-calculationsDrug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide + Quiz | KnowledgeDose Sep 20, 2019 · Drug Dosage Calculation Formulas. To calculate the number of tablets, use the following formula: Strength required / Stock strength = Number of tablet(s) required. Or another way this drug dosage formula can be expressed is: What you want / What you’ve got = Number of tablet(s) required. To calculate the volume dose for liquid medicine, use this formula: (Strength required / Stock strength) × Stock volume = Volume dose required Medication Administration: NCLEX-RN || RegisteredNursing.org The dosage of the medication; The side effects of the medication; The possible adverse effects of the medication; How and where the medication should be safely stored, such as in the refrigerator or in a dark place, for example; The importance of and the method for checking the medication's label for the name, dose, and expiration date › books › NBK493162Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method ... Mar 09, 2022 · A basic formula, solving for x, guides us in the setting up of an equation: D/H x Q = x, or Desired dose (amount) = ordered Dose amount/amount on Hand x Quantity. For example, a provider requests lorazepam 4 Mg IV Push for a patient in severe alcohol withdrawal. The clinician has 2 mg/mL vials on hand.
IV Flow Rate Calculation Reviewer & Quiz (60 Questions) - Nurseslabs The nursing test bank for IV flow rate calculations below is separated into two sets of quizzes. Included topics are IV flow rate calculation, calculating for drops per minute, calculating for milliliters per hour, and total infusion time. If you need a quick review, please read the IV flow rate reviewer below.
Difference Between Drug Dose and Dosage - Verywell Health By contrast, the dosage is how to take the medication as prescribed: a specific amount, number, and frequency of doses over a specific period of time. In other words, a dose is simply an amount of a medication you take at one specific time. The dosage is the dose, or amount of drug, plus when and how often to take it.
› en-us › documentDosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter. Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution. a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d. Route e. Dosage strength f. Diluent and amount. Reading Drug Labels. a. Route b. Dosage strength c. Single or multi-dose. Reading Drug Labels. Order: Phenytoin 15 mg/kg x1 loading dose
Drug Calculations: How to Calculate Drops Per Minute Cancel the labels. What you are left with are drops (gtts) multiplied by the infusion rate divided by 60. You can rearrange the equation and divide the drops (gtts) by 60 and multiply by infusion rate. Since all the drip factors are easily divisible into 60, you can simply divide the infusion rate by the following factors.
Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN || RegisteredNursing.org Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg How many tablets should be administered daily? In this problem you have to determine how many tablets the patient will take if the doctor order is 125 mg a day and the tablets are manufactured in tablets and each tablet has 250 mg. This problem can be set up and calculated as shown below.
Dosage Forms | FDA NCI Thesaurus OID: 2.16.840.1.113883.3.26.1.1. NCI concept code for pharmaceutical dosage form: C42636
webcontent.indianhills.edu › lu03_calculationsFormulas for Calculating Medication Dosage Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage Basic Formula D -- x Q = X A Where D (desired) is the dosage the physician ordered, A (available) is the dosage strength as stated on the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters).
ATI Dosage Calculations Practice-Answer Key 2020/2021 - Stuvia ATI Dosage Calculations Practice-Answer Key 2020/2021 ATI Dosage Calculations Practice-Answer Key 1. Furosemide 50mg IV push now. Available: Furosemide 40mg/10mL How many mL will you give? Answer 12.5 2. The IV order is for D5W to infuse at 100 mL/hr. The drop factor is 10 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute (gtt/min) should the IV be ...

The 25+ best Dosage calculations ideas on Pinterest | Nursing calculations, Nursing math and ...
Medical Dosage Calculations For Dummies Cheat Sheet flow rate (mL/hr) = total volume (mL) ÷ infusion time (hr) flow rate (mL/hr) = 1,000 ÷ 4 flow rate (mL/hr) = 250 The flow rate is 250 mL/hr. Common conversion factors in medical dosage calculations As a healthcare professional, you have to convert patient weights, fluid volumes, medication weights, and more.

Medication Dosage Calculation.pdf - Medication Dosage Calculation mapharm.com\/dosage_calc.htm ...
Pharmacology Calculations & Conversions - Study.com What are the steps in calculating drug dosages? First, ensure that the conversions are done correctly. Then, identify the values in the Desired/ Have x Quantity Formula. Finally, solve for that...
Tylenol Dosage Calculator for Infants and Children Use the syringe or dosing cup that came with your medication and measure out your child's dose. For example, if you are using Infants' Tylenol Oral Suspension, which has a concentration of 160 mg per 5 ml, the correct dosages are: 6 to 11 pounds = 1.25 ml or 40 mg 12 to 17 pounds = 2.5 ml or 80 mg 18 to 23 pounds = 3.75 ml or 120mg
The Medication Dispensing Process for Pharmacists - Study.com Step Three: Label and Prepare the Medication. A great way to avoid errors is to create the label for the medication as soon as you have everything validated and clarified. By printing the date of ...
› health › dosageDosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? May 08, 2022 · Determine the dosage of the medication. Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid?
Dosage Calculations FINAL Exam Version 1 Exam (elaborations) - Stuvia Dosage Calculations FINAL Exam Version 1 Exam (elaborations) 1. Furosemide 50mg IV push now. Available: Furosemide 40mg/10mL How many mL will you give? 2. The IV order is for D5W to infuse at 100 mL/hr. The drop factor is 10 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute (gtt/min) should the IV be regulated? 3. 4 Tablespoons = teaspoons? 4.
Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method Article A basic formula, solving for x, guides us in the setting up of an equation: D/H x Q = x, or Desired dose (amount) = ordered Dose amount/amount on Hand x Quantity. For example, a provider requests lorazepam 4 Mg IV Push for a patient in severe alcohol withdrawal. The clinician has 2 mg/mL vials on hand.
Clinical Calculations: Module 5: Parenteral Medications You will calculate the correct amount of injectable medications to give a client. Assume all questions ask for the amount per dose unless instructed otherwise. Equivalents to know You should now know all your commonly used equivalents. Rounding rules to know You will continue to use the rounding rules for numbers >1 and <1.
Medications | Health Literacy | CDC Medication Labels. A study published in 2013 external icon finds a patient-centered label was better at preventing participants from exceeding the maximum dose in 24 hours, compared to a standard label. The patient-centered label did not significantly reduce other dosing errors such as taking more than two pills at a time and waiting fewer than four hours between doses.








Post a Comment for "45 dosage calculations from medication labels"